VPC is a game-changing concept that allows businesses to create their private, isolated cloud environments within a larger cloud infrastructure. This level of customization and security enables companies to tailor their cloud resources to meet specific needs, ensuring data protection and seamless integration with existing IT infrastructure.
Join us as we showcase real-world use cases of VPC in action, from deploying web applications with enhanced security to creating multi-tiered architectures for enterprise solutions. Uncover the benefits of VPC, such as improved network performance, reduced costs, and simplified management. Let’s explore how VPC can transform your cloud experience, providing you with the tools and insights to leverage this technology for a more efficient, secure, and successful cloud journey. Embrace the Virtual Private Cloud and unlock a world of possibilities for your organization.
To understand the concept of the VPC, first, we have to grasp the idea of Cloud and Cloud computing. Cloud computing is a virtual network that works as storage, a pool of resources, and/or provides computing power. The company that buys a cloud computing service does not have to worry about managing such a huge online platform. Companies lend cloud services by a “pay as you go” model, so it might decrease capital expenditure, but an unsuspecting user might rapidly increase the operation fees. Large cloud services are scattered through different locations called data centers.
The goal of cloud computing is for layman users to take benefits without knowing any rocket science behind tough things. The main working force behind cloud computation is its Virtualization. It virtualizes different devices which can compute a task at once. It creates a system of multiple devices that work together, and idle computing resources can be used accordingly, and we get maximum efficiency through this.
All the work is done internally, and we just have to give commands and not worry about how the task is done. In such a manner, big databases can be created that can be shared over public or private users. These users can use this data, data storage, resources, and computing power individually from all over the world. Using different subnet IPs can be personalized and private, although it is connected to multiple users. All these users can reap benefits from this cloud service. In technology industries, this can improve the time elapsed for a work to be done and functions; structures can be added, reworked, and edited by many, and thus planning will be updated in real-time. It also ensures independence and remote location service for its users.
A Virtual Private Cloud is a system of resources in a public domain that isolates its different users by giving them a sense of privacy. A VLAN or a bunch of encrypted communication channels unique to every user ensures that every user is separated from other users of the same private cloud or the public pool. It comes with a VPN function, providing isolation, authentication, remote access, and encryption of the shared but private cloud database. A cloud infrastructure that is not shared with other users or the company that effectively uses it is called the Virtual Private Cloud (VPC). Amazon Private Cloud by AWS was launched in 2009, and then IBM, and Google followed suit.
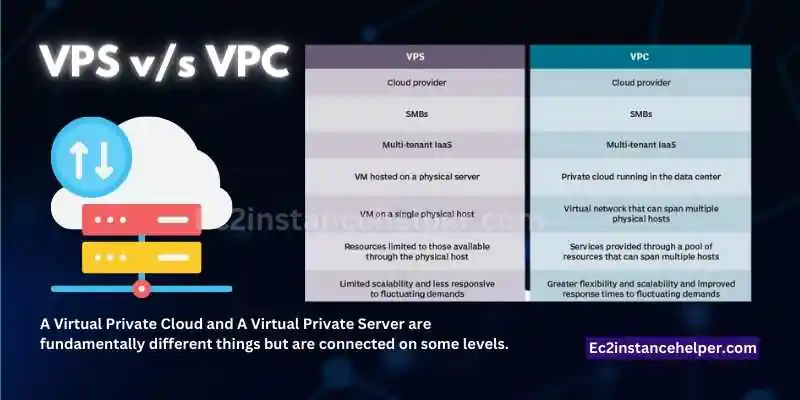
VPS v/s VPC
A Virtual Private Cloud and A Virtual Private Server are fundamentally different things but are connected on some levels. We have already learned how VPC is used. VPS is used for various purposes ranging from hosting websites to hosting remote applications. It means sharing resources on the main server, and it is also the data center. The other hosts can work and compute independently; each of them is a Virtual Private Server. Some examples are- GoDaddy, 1&1, Hostgator, etc. A VPS is a giant server whose instances are split so each component can function separately and independently. So, layers are created to separate and make every component an independent, standalone server. So VPS is a virtual technology by which you can run your websites or applications but stay in the same system although all of its standalone and gain superuser level access for each user. It shares computing resources.
On the other hand, VPC shares data, storage, and computing power. It is a pool of storage where each user is given enough privacy, and yet they are connected. There is no main host in VPC but different data centres, whereas, in VPS, there is one data centre called the main host.
|
Our overall ratings are based on the average score of all ratings combined. |
Max RAM | Max CPUs |
|
InMotion |
A2 Hosting | Bluehost |
| 4.5 | 4.3 |
4.2 |
|
14GB |
32GB | 8GB |
| 14 | 8 |
4 |
|
10TB |
4TB | 3TB |
| YES | YES |
YES |
|
300GB |
450GB | 120GB |
| 99.97% | 99.95% |
99.98% |
(Source: Internet)
VPN v/s VPC
A VPN gives a company network access to public networks such as the Internet. It is a Virtual Private Network. A VPN is used to share data efficiently over different public networks from private networks as it is connected to both. It ensures guaranteed security and privacy of data through data encryption and other mechanisms. However, commercial VPNs are used to hide an individual user’s IP address and location by channeling all secure traffic through a secure tunnel. We can hide behind VPNs to see data that is banned or blocked by one country or geographical place, use torrents or browse private content. Many VPNs offer free services to fight against current trends of megalomaniac control frenzy by several governments. Free VPN services are unreliable and inefficient or come with time and/or data limits. So, even though VPC and VPN sound similar, there is nothing in common. VPC is a shared resource pool, and VPN is a mask.
|
Service |
Monthly price | Servers and countries |
| Hotspot Shield | $12.99/mo. |
3,200+ servers 80+ countries |
|
Surfshark |
$12.95/mo. | 3,200+ servers 65 countries |
| IPVanish | $10.99/mo. |
1,900+ servers 52 countries |
|
PureVPN |
$10.95/mo. |
6,500+ servers 140+ countries |
Public VPC v/s Private VPC
A public VPC can send traffic directly to the internet, whereas a Private one cannot. A public subnet can route all traffic through IGW, i.e., Internet Gateway. It has no constraints on bandwidth. IGW can also receive inbound traffic if the security mechanisms match. However, if it is a private subnet, then it needs to go through a NAT, i.e., Network Address Translation Gateway. Your wireless router uses a NAT. NAT does not allow inbound traffic. Thus a Virtual Private Cloud stays private.
Security Measures for Your VPC
Any guidelines cannot represent a solution, but these are the best practices to keep your VPC secure and running. These are considerations as everywhere the same techniques or resources won’t be available.
- To increase your availability, use multiple deployment zones.
- Read about and use network ACLs and security groups.
- Use your policies to control and restrict access.
- Use a tool to watch over VPC components and active VPNs.
- Use flow logs to track and record inbound and outbound IP addresses and traffic going in and out from the VPC.
VPC network v/s VPC peering
A VPC is an isolated network within a cloud provider. A VPC peering is a network connection between two or more VPC using private and secure traffic sharing. It improves security as it makes a connection between more VPCs but blocks the internet. VPC network similarly connects you to several VPC peers, sharing data, security details, resources, or computing power without accessing the internet. It makes VPC more flexible and efficient. It is a virtual version of a physical network. It is normally used in the backend.
Reasons for transitioning to VPC
Just like things were in your old data center, VPC is needed to secure and share your data to a closed group, away from the touch of the internet. It is the root to connect back to legacy data centers. No VPNs, hardware, or data centers are required to use a VPC. From the point of view of security mechanisms and tactics, VPC is not a magical shield but another added layer of responsibility. VPCs give you extra security tools such as flow logs, but we must learn how to use them. Some primary research from our end is needed here. However, it does not provide internal protection once the data is in the network. Some app developers need some software or services that only run on a VPC – in those cases, VPC is an absolute necessity. Now, we will look at some reasons why should one use a VPC:
Security measures:
A VPC keeps you isolated from the internet. You can use data, storage, resources, and computing power remotely without any hardware implementation. Blocking the internet gives you an extra layer of security and privacy.
Connected Data Centre:
It helps you to connect your data center with a network. It can work as a backup to your most important data centers. In case of disasters, you would not face any lag or downtime as the data inside VPC will be up and running nonetheless. It also adds disaster recovery services to protect your network from downfall.
Everything is not Web-based:
The internet is a jungle, and the animals are viruses and hackers and data leaks that fester the internet and gradually your network if it is connected its data to the internet. Not all parts of your application are needed to be exposed to the internet or its evils. But by using security groups, custom policies, and similar security mechanisms, you can build your app over separate VPC peers and enrich it more. In a multi-tiered situation, where an app uses several databases and networks to operate, VPC lets you implement security protocols to those shared databases and networks and keeps them out of the internet’s hands. Thus, your app development stays secure and private, although you use a vast resource pool to build things.
Security Groups;
Security groups are like a firewall. In a VPC, the security group decides which instances can talk or connect, i.e., send inbound and/or outbound data to and from. If two security groups match, then by impending some more restrictions and custom control – two or more VPCs can connect between them and share resources without relying on the internet at all.

Practical Use-Cases for VPC applications
Web Hosting and Application Deployment
VPCs are extensively used for hosting websites and deploying web applications. Businesses can create isolated VPC environments to host their websites and applications securely, ensuring optimal performance and scalability.
Data Analytics and Big Data Processing
VPCs provide an ideal platform for data analytics and big data processing. Organizations can deploy complex data processing frameworks in a controlled and secure VPC environment, enabling them to handle large datasets and perform data-intensive tasks efficiently.
Enterprise Applications and Services
Many enterprises utilize VPCs to host critical business applications and services. VPCs enable businesses to set up private networks with controlled access, allowing seamless communication between various components of their applications.
DevOps and Continuous Integration
VPCs play a crucial role in DevOps and continuous integration (CI) workflows. Development teams can create isolated VPCs for testing and staging environments, ensuring that software updates and changes are thoroughly tested before deployment.
Disaster Recovery and Backup Solutions
VPCs are often employed for disaster recovery and backup solutions. Organizations can set up secondary VPCs in different geographical regions, ensuring data redundancy and resiliency in case of an outage in the primary environment.
Internet of Things (IoT) Applications
VPCs facilitate the secure deployment of IoT applications by providing a segregated environment to manage and process data from connected devices. This ensures data privacy and prevents unauthorized access.
Hybrid Cloud Deployments
VPCs are instrumental in hybrid cloud setups, allowing seamless integration between on-premises infrastructure and public cloud resources. This integration enables businesses to extend their existing infrastructure into the cloud environment while maintaining consistent networking policies.
Media Streaming and Content Delivery
VPCs are employed to deliver media content efficiently and securely. By setting up dedicated VPCs for content delivery networks (CDNs), businesses can ensure high-performance streaming and reduced latency for users worldwide.
Testing and Quality Assurance
VPCs offer an isolated environment for testing and quality assurance activities. Organizations can replicate production environments in VPCs, enabling teams to conduct testing without affecting the live systems.